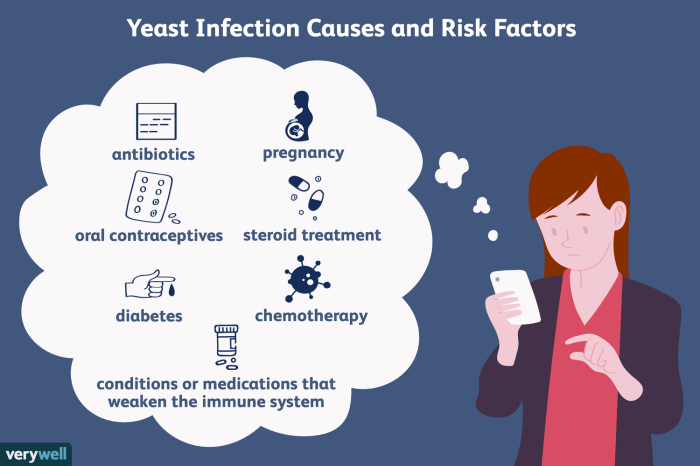
Do antivirals cause yeast infections – The use of antiviral medications has become increasingly common in recent years, raising concerns about their potential side effects. One of the most common concerns is the development of yeast infections. This article delves into the relationship between antivirals and yeast infections, examining the evidence and providing guidance on risk mitigation strategies.
Antivirals are a class of medications used to treat viral infections. They work by inhibiting the replication of viruses, preventing them from multiplying and causing infection. However, some antivirals have been associated with an increased risk of yeast infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or those taking high doses of the medication.
Impact of Antivirals on Yeast Infection Development
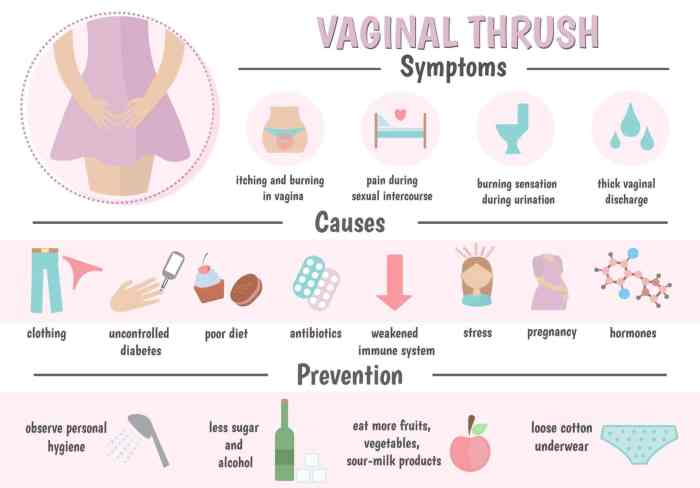
Antiviral medications are commonly used to treat viral infections, such as HIV, hepatitis, and herpes. However, their use has been associated with an increased risk of developing yeast infections, particularly among individuals with compromised immune systems.
Studies have shown that individuals taking antivirals have a significantly higher prevalence of yeast infections compared to those not taking these medications. The risk of yeast infection is particularly high among individuals taking nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), a class of antivirals commonly used for HIV treatment.
Antivirals may contribute to yeast infection formation through several mechanisms. They can alter the balance of the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to opportunistic infections like yeast infections. Additionally, some antivirals may have direct antifungal activity, which can lead to the overgrowth of yeast.
Specific Antivirals and Yeast Infection Risk
Not all antivirals carry the same risk of yeast infections. NRTIs, as mentioned earlier, have been strongly associated with an increased risk. Specific NRTIs such as lamivudine and emtricitabine have been found to be more likely to cause yeast infections than others.
Protease inhibitors (PIs), another class of antivirals used for HIV treatment, have a lower risk of causing yeast infections compared to NRTIs. However, some PIs, such as indinavir and nelfinavir, have been associated with an increased risk.
The risk of yeast infection while taking antivirals depends on several factors, including the type of antiviral medication, the dosage, and the duration of treatment. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or undergoing chemotherapy, are at a higher risk.
Risk Mitigation Strategies, Do antivirals cause yeast infections
To reduce the risk of yeast infections while taking antivirals, several strategies can be employed:
- Antifungal prophylaxis:Antifungal medications can be prescribed to prevent yeast infections in individuals at high risk, such as those taking NRTIs.
- Maintaining good hygiene:Practicing good hygiene, including regular bathing and wearing clean clothes, can help reduce the risk of yeast infections.
- Proper nutrition:Maintaining a healthy diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of infections.
Alternative Treatment Options
For individuals who develop yeast infections while taking antivirals, several treatment options are available:
- Topical antifungals:Creams, ointments, or suppositories containing antifungal medications can be used to treat yeast infections. These medications are applied directly to the affected area.
- Oral antifungals:Oral medications, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, can be used to treat more severe yeast infections.
- Lifestyle modifications:Making lifestyle changes, such as avoiding sugary foods and wearing loose-fitting clothing, can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of recurrence.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment option based on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health.
Patient Education and Awareness
Educating patients about the potential risk of yeast infections associated with antiviral use is crucial. Healthcare providers should provide clear and accurate information to patients about the symptoms of yeast infections, the importance of early detection and treatment, and the available preventive measures.
Patients should be encouraged to report any symptoms of a yeast infection to their healthcare provider promptly. Resources, such as patient education materials and online support groups, can help patients stay informed and manage their condition effectively.
FAQ Insights: Do Antivirals Cause Yeast Infections
Can all antivirals cause yeast infections?
No, not all antivirals cause yeast infections. The risk varies depending on the specific antiviral medication, the dosage, and the individual’s susceptibility to yeast infections.
What are the symptoms of a yeast infection?
Symptoms of a yeast infection can include itching, burning, redness, and discharge in the affected area.
How can I reduce my risk of developing a yeast infection while taking antivirals?
To reduce your risk, maintain good hygiene, wear loose-fitting clothing, and avoid sugary foods and drinks. Your doctor may also recommend antifungal prophylaxis.