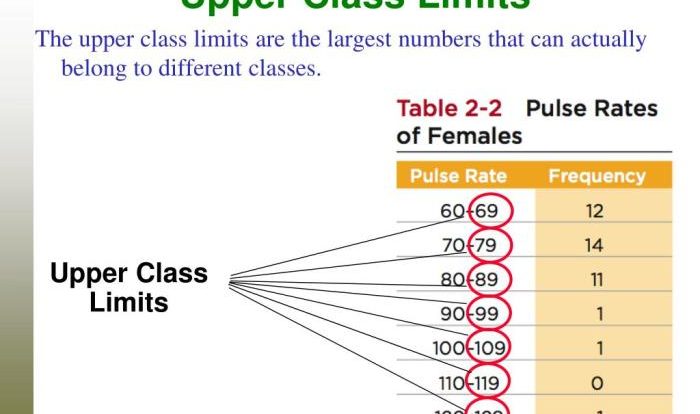
Introducing the mathematical statistics and data analysis solutions PDF, a comprehensive resource that delves into the fundamental concepts, techniques, and applications of statistical analysis. This guide empowers readers with the knowledge and tools to harness the power of data, unlocking valuable insights and driving informed decision-making.
Within this meticulously crafted document, you will embark on a journey through the realm of statistical distributions, parameter estimation, hypothesis testing, data collection, preparation, analysis, and interpretation. Real-world examples and case studies bring these concepts to life, showcasing the transformative impact of statistical analysis across diverse industries.
1. Mathematical Statistics

Mathematical statistics is a branch of mathematics that deals with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. It provides a framework for understanding the underlying patterns and relationships in data, allowing us to make informed decisions and predictions.
Statistical distributions are mathematical models that describe the probability of occurrence of different outcomes. Common statistical distributions include the normal distribution, binomial distribution, and Poisson distribution. These distributions have wide applications in fields such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Parameter Estimation
- Point estimation: Estimating a population parameter using a single value.
- Interval estimation: Estimating a population parameter within a range of values.
Hypothesis Testing
- Null hypothesis: A statement that there is no significant difference or effect.
- Alternative hypothesis: A statement that contradicts the null hypothesis.
- Significance level: The probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
2. Data Analysis
Data analysis is the process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data to extract meaningful insights. It helps us understand the structure, patterns, and trends in data, enabling us to make informed decisions and predictions.
Data Collection and Preparation, Mathematical statistics and data analysis solutions pdf
- Data collection: Gathering data from various sources, such as surveys, experiments, and sensors.
- Data cleaning: Removing errors, inconsistencies, and duplicate data.
- Data transformation: Converting data into a suitable format for analysis.
Data Analysis Techniques
- Statistical modeling: Building mathematical models to represent the underlying relationships in data.
- Machine learning: Using algorithms to train models that can make predictions or classify data.
3. Applications of Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis

Mathematical statistics and data analysis are widely used in various fields, including:
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient data to improve diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes.
- Finance: Assessing risk, forecasting financial trends, and optimizing investment strategies.
- Marketing: Understanding customer behavior, segmenting markets, and developing targeted campaigns.
Benefits
- Informed decision-making: Data-driven insights help organizations make better decisions.
- Improved predictions: Statistical models can predict future outcomes and trends.
- Optimization: Data analysis can identify areas for improvement and optimize processes.
4. Tools and Resources for Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis: Mathematical Statistics And Data Analysis Solutions Pdf
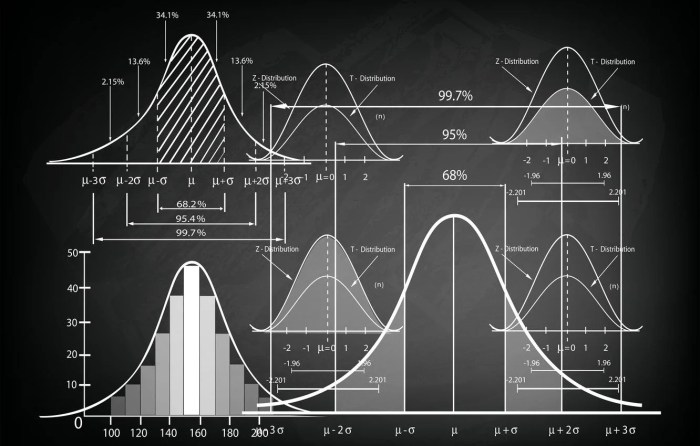
Numerous software packages and programming languages are available for statistical analysis, including:
- R: A free and open-source statistical programming language.
- Python: A versatile programming language with extensive statistical libraries.
- SPSS: A commercial software package specifically designed for statistical analysis.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Software | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| R | Free and open-sourceLarge community supportCustomizable | Can be complex for beginnersLess user-friendly interface than commercial software |
| Python | Versatile and powerfulWide range of librariesGrowing data science community | Can be more complex to learn than RMay require additional packages for specific statistical functions |
| SPSS | User-friendly interfaceExtensive statistical capabilitiesWidely used in industry | Commercial software (not free)Less customizable than R or PythonMay not be suitable for advanced statistical analysis |
5. Future Trends in Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis

The field of mathematical statistics and data analysis is constantly evolving, with emerging trends and advancements:
Big Data Analytics
The increasing volume and complexity of data require new techniques for handling and analyzing big data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling more accurate predictions and insights.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing platforms provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for data analysis and storage.
FAQ Insights
What is the purpose of mathematical statistics?
Mathematical statistics provides a framework for understanding the underlying patterns and relationships within data, enabling researchers to make inferences and draw conclusions based on observed data.
How is data analysis used in decision-making?
Data analysis empowers decision-makers with data-driven insights, enabling them to make informed choices based on objective evidence rather than intuition or guesswork.