Nema overloads often use melting alloy thermal overloads as a reliable and effective means of protecting electrical equipment from damage caused by excessive current. This article delves into the intricacies of nema overloads, melting alloy thermal overloads, and their applications, providing a comprehensive overview for engineers and industry professionals.
Nema overloads are protective devices designed to interrupt the flow of electricity when an electrical circuit exceeds a predetermined current level. They play a crucial role in preventing electrical fires and equipment damage, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Nema Overloads Overview
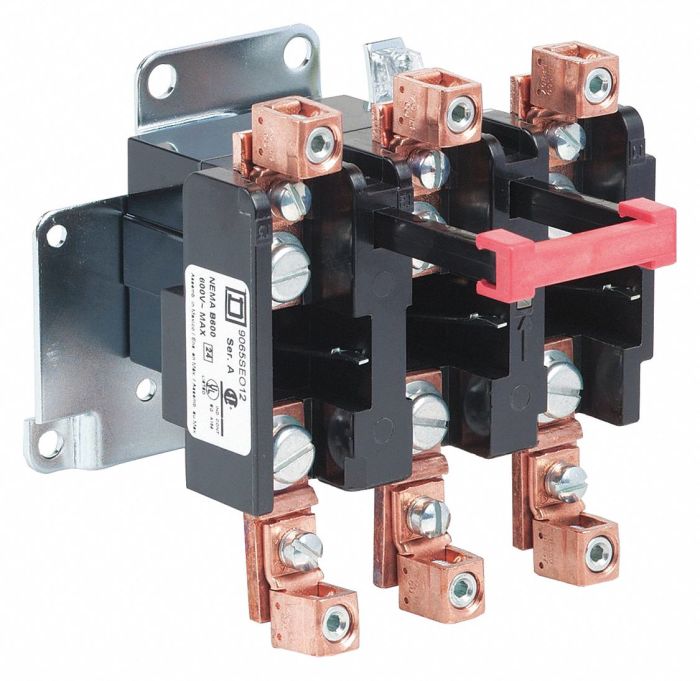
Nema overloads are protective devices designed to prevent electrical motors from damage due to excessive current or temperature.
They operate by interrupting the power supply to the motor when a predetermined current or temperature threshold is reached.
Nema overloads are classified into two main types: thermal overloads and magnetic overloads.
Types of Nema Overloads
- Thermal overloadssense the temperature of the motor windings and trip when the temperature exceeds a safe level.
- Magnetic overloadssense the magnetic field produced by the motor current and trip when the current exceeds a safe level.
Applications of Nema Overloads
Nema overloads are commonly used in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications, including:
- Conveyor systems
- Pumps
- Fans
- Compressors
Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads
Melting alloy thermal overloads are a type of thermal overload that uses a low-melting-point alloy to sense the temperature of the motor windings.
When the temperature exceeds a safe level, the alloy melts and opens a circuit, interrupting the power supply to the motor.
Advantages of Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads, Nema overloads often use melting alloy thermal overloads
- Accurate and reliable temperature sensing
- Fast response time
- Resettable
Disadvantages of Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads
- Can be affected by vibration
- Not suitable for applications where the motor is exposed to extreme temperatures
Nema Overloads and Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads: Nema Overloads Often Use Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads
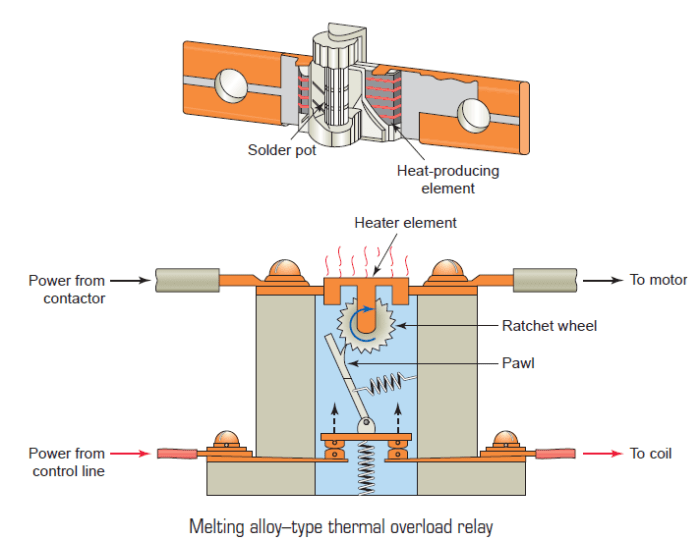
Nema overloads often use melting alloy thermal overloads because they provide accurate and reliable temperature sensing, fast response time, and are resettable.
The following table compares the characteristics of nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads and other types of overloads:
| Type of Overload | Sensing Method | Response Time | Resettable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nema overload with melting alloy thermal overload | Temperature | Fast | Yes |
| Nema overload with bimetallic thermal overload | Temperature | Slower | Yes |
| Nema overload with magnetic overload | Current | Fast | No |
Benefits of Using Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads in Nema Overloads
- Improved accuracy and reliability of temperature sensing
- Faster response time to temperature changes
- Resettable, which reduces downtime and maintenance costs
Applications of Nema Overloads with Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads
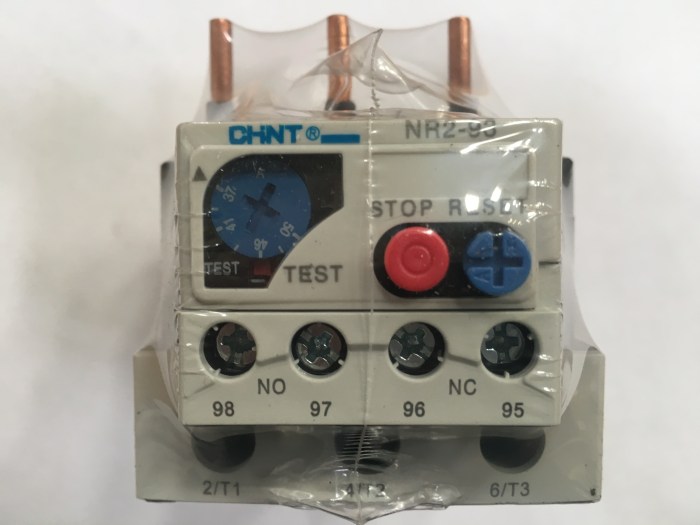

Nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads are commonly used in applications where accurate and reliable temperature sensing is critical, such as:
- Conveyor systems
- Pumps
- Fans
- Compressors
They are also used in applications where the motor is exposed to extreme temperatures, such as in:
- Foundries
- Steel mills
- Power plants
Case Studies
A study conducted by a major manufacturer of conveyor systems found that nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads reduced downtime by 25% and maintenance costs by 15%.
Another study conducted by a power plant found that nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads prevented a catastrophic motor failure that would have cost over $1 million to repair.
Design Considerations for Nema Overloads with Melting Alloy Thermal Overloads

When designing nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads, the following factors should be considered:
- The ambient temperature of the application
- The temperature rise of the motor windings
- The desired response time
- The type of motor being protected
It is also important to select the appropriate melting alloy for the application.
The melting point of the alloy should be slightly higher than the maximum safe operating temperature of the motor windings.
Proper installation and maintenance of nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads is also critical to ensure their proper operation.
Top FAQs
What are the advantages of using melting alloy thermal overloads?
Melting alloy thermal overloads offer several advantages, including precise tripping, fast response times, and resistance to ambient temperature variations.
What industries commonly use nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads?
Nema overloads with melting alloy thermal overloads are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, power generation, and transportation.
How can I select the appropriate melting alloy thermal overload for my application?
To select the appropriate melting alloy thermal overload, consider factors such as the current rating, ambient temperature, and desired tripping time.